10 Things you need to know about solar in 2024
History:
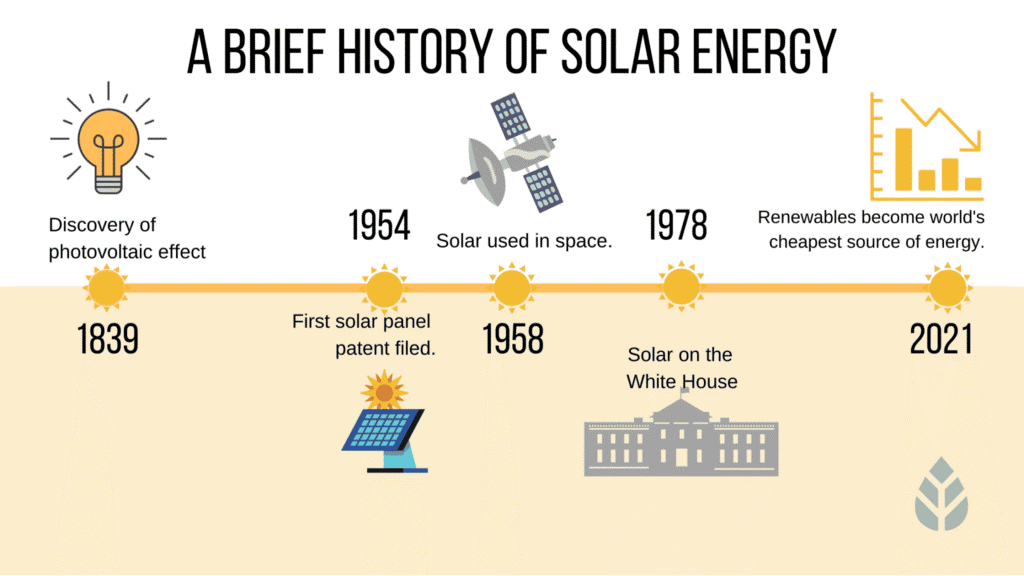
The history of solar power dates back several centuries, with the basic principles of converting sunlight into usable energy being understood and utilized in various ways. Here's a brief overview of the key milestones in the history of solar power:
a. Ancient Solar Architecture (7th Century BC): Ancient civilizations, such as the Greeks and Chinese, used architectural design principles to capture and utilize solar energy for heating. South-facing windows and building materials with high thermal mass were employed to optimize sunlight absorption.
b. Solar Furnaces (3rd Century BC): The ancient Greeks, including the mathematician and inventor Archimedes, used mirrors to focus sunlight onto a single point, creating a solar furnace. This early use of concentrated solar power was employed for various applications, including warfare.
e. Albert Einstein's Photoelectric Effect Theory (1905): Albert Einstein explained the photoelectric effect, providing a theoretical foundation for understanding the conversion of light into electricity. This work later contributed to the development of solar cells.
f. Bell Labs' Silicon Solar Cell (1954): Bell Labs researchers Daryl Chapin, Calvin Fuller, and Gerald Pearson developed the first practical photovoltaic (PV) or solar cell using silicon. This marked a significant improvement in efficiency and laid the foundation for the modern solar industry.
f. Bell Labs' Silicon Solar Cell (1954): Bell Labs researchers Daryl Chapin, Calvin Fuller, and Gerald Pearson developed the first practical photovoltaic (PV) or solar cell using silicon. This marked a significant improvement in efficiency and laid the foundation for the modern solar industry.
g. Early Space Applications (1950s-1960s): Solar cells were used to power satellites and spacecraft. The Vanguard 1 satellite, launched in 1958, was equipped with a small array of solar cells, making it the first artificial satellite to use solar power.
h. Solar-Powered Calculators (1970s): The development of small, efficient solar cells led to their use in calculators and other small electronic devices during the 1970s. This helped popularize the technology and improve manufacturing processes.
i. Energy Crisis and Solar Research (1970s): The oil crises of the 1970s prompted increased interest in renewable energy sources, including solar power. Governments and research institutions worldwide began investing in solar research and development.
j. Grid-Connected Solar Systems (1980s-1990s): The development of grid-connected solar systems allowed solar-generated electricity to be fed back into the grid. This made solar power a viable option for residential and commercial applications.
k. Cost Reductions and Global Growth (2000s-Present): Advances in technology, increased production scale, and supportive government policies have contributed to a significant reduction in the cost of solar panels. Solar power capacity has grown rapidly worldwide, with solar becoming an increasingly competitive source of energy.
l. Technological Innovations (Present): On-going research focuses on improving solar cell efficiency, exploring new materials, and developing innovative solar technologies, such as thin-film solar cells, solar paint, and flexible solar panels.
The history of solar power reflects a gradual progression from ancient passive solar applications to the highly efficient and widespread use of photovoltaic technology today. Continued advancements in solar technology and increased global adoption contribute to the on-going evolution of solar power as a key component of the world's energy mix. These milestones highlight the long and diverse history of solar power, from ancient uses to modern technological advancements.
2. Why Solar system is recommended?
The recommendation of a solar power system is based on several advantages and benefits associated with harnessing energy from the sun. Here are some key reasons why solar power systems are often recommended:
Renewable and Sustainable: Solar energy is a renewable and virtually limitless resource. The sun is expected to continue radiating energy for billions of years, making solar power a sustainable and environmentally friendly option for electricity generation. Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Solar power systems produce electricity without emitting harmful greenhouse gases, unlike traditional fossil fuels. By reducing dependence on non-renewable energy sources, solar power helps mitigate climate change and air pollution. Lower Electricity Bills: Installing a solar power system allows homeowners, businesses, and institutions to generate their own electricity, reducing reliance on grid power. This can lead to significant savings on electricity bills over the system's lifespan. Energy Independence: Solar power systems provide a degree of energy independence. By generating electricity on-site, users become less reliant on external energy sources and are better prepared to handle potential disruptions to the power grid. Financial Incentives and Rebates: Many governments offer financial incentives, tax credits, and rebates to encourage the adoption of solar power. These incentives can significantly offset the initial cost of installing a solar system, making it a more attractive investment. Low Operating and Maintenance Costs: Solar panels have minimal operating and maintenance costs. Once installed, they require relatively little upkeep, and their lifespan is typically several decades. This makes solar power a cost-effective and low-maintenance energy solution. Grid Support and Net Metering: In regions with net metering policies, excess electricity generated by a solar system can be fed back into the grid. This allows users to earn credits or receive compensation for the surplus energy they produce. Technological Advancements: On-going advancements in solar technology continue to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and expand the range of applications. Innovations in energy storage, smart grid integration, and solar panel design contribute to the overall effectiveness of solar power systems Job Creation and Economic Growth: The growing solar industry creates jobs in manufacturing, installation, maintenance, and research. The development and deployment of solar power contribute to economic growth while promoting a cleaner energy future. Environmental Benefits: Solar power generation has minimal environmental impact compared to conventional energy sources. It reduces air and water pollution, minimizes habitat disruption, and helps conserve natural resources. Resilience to Power Outages: Solar power systems with energy storage capabilities can provide a reliable source of electricity during power outages. This can be particularly important for critical facilities and individuals seeking greater resilience in their energy supply. Community and Corporate Sustainability Goals: Solar adoption aligns with sustainability goals for both communities and corporations. Many entities commit to using renewable energy sources to reduce their carbon footprint and contribute to a more sustainable future. While there are numerous advantages to solar power, it's essential to consider factors such as site suitability, upfront costs, and local regulations when deciding whether to invest in a solar system. The feasibility and benefits can vary based on location, energy needs, and individual circumstances
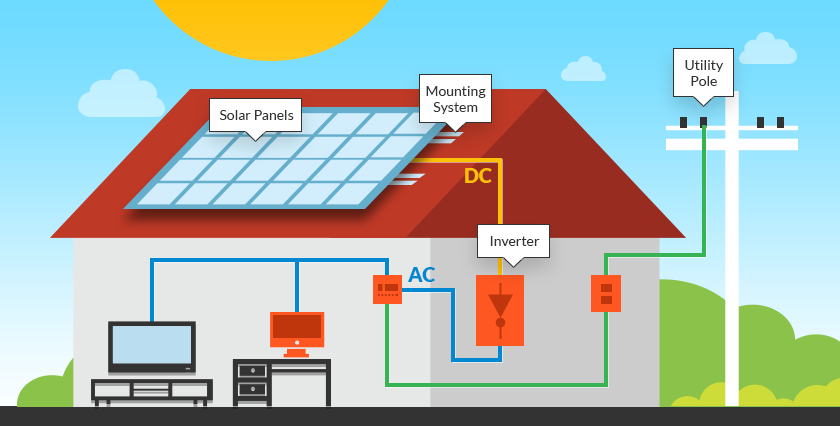

3. Durability of solar
The durability of a solar power system depends on various factors, including the quality of the components, the installation process, and maintenance practices. Here are key considerations regarding the durability of a solar system:
Solar Panel Lifespan: High-quality solar panels typically have a lifespan of 25 to 30 years or more. Most manufacturers offer warranties for this duration. Solar panels gradually degrade over time, but reputable manufacturers provide performance guarantees that ensure a certain level of power output over the warranty period. Inverter Lifespan: Inverters are essential components in a solar power system, converting DC electricity generated by solar panels into AC electricity for use in homes or businesses. Inverters typically have a shorter lifespan than solar panels, ranging from 10 to 20 years. It's important to choose a reliable inverter and consider potential replacement costs. Frame and Mounting Structure: The durability of the frame and mounting structure is crucial for the long-term stability of the solar panels. High-quality materials, such as corrosion-resistant aluminum or stainless steel, are often used to ensure resistance to weathering and environmental conditions. Weather Resistance: Solar panels are designed to withstand various weather conditions, including rain, snow, hail, and high winds. Panels undergo rigorous testing to ensure they can endure harsh weather, and they are rated for specific wind and snow loads. Installers should follow industry best practices to secure panels against extreme weather events. Quality of Installation: The installation process is critical for the overall durability and performance of the solar system. Properly trained and experienced installers follow guidelines to ensure secure mounting, correct wiring, and effective weatherproofing. Poor installation practices can lead to premature wear and tear. Maintenance Practices: Regular maintenance can extend the life of a solar power system. This may include cleaning the panels to remove dust and debris, checking for any loose connections, and ensuring the inverter is functioning correctly. Periodic professional inspections are also recommended. Environmental Factors: The location and environmental conditions can impact the durability of a solar system. Systems in areas with high humidity, extreme temperatures, or significant pollution may experience different rates of degradation. Selecting components designed for specific environmental conditions is important. Quality of Components: The durability of a solar system is heavily influenced by the quality of its components, including solar panels, inverters, and mounting hardware. Choosing products from reputable manufacturers with a track record of reliability is crucial. Technological Advances: Ongoing advancements in solar technology may lead to more durable and efficient components. Keeping abreast of technological developments can inform decisions when considering the installation or upgrade of a solar power system. Warranty and Support : Assess the warranties provided by manufacturers and installers. Reputable solar panel manufacturers often offer performance guarantees and product warranties. Ensure that the installer provides warranty support and has a reputation for standing behind their work. Overall, a well-designed, professionally installed, and properly maintained solar power system can be highly durable and provide reliable energy generation for many years. It's important for consumers to do thorough research, work with reputable installers, and consider the long-term performance and durability of the components when investing in a solar system.

4. Solar power will not be the only source of electricity
If you choose an on-grid solar system, your home will be connected to your city’s electricity grid to make sure a continuous source of power when required. This is especially helpful if you live in a place that doesn’t have rational sunlight or where sunlight is not ample many months out of the year. Some property owners choose to live off the grid, depending on battery storage and generators. This type of installation will require a professional and experienced solar panel installer who knows how to do this.

5. Which type of installation is best for you: Rooftop solar system, or ground-mount?
The choice between a rooftop solar system and a ground-mounted system depends on various factors, including your specific needs, available space, and preferences. Here are some considerations to help you decide which type of installation is best for you:
Rooftop Solar System:
Space Constraints: Advantage: Rooftop systems are ideal if you have limited land space. They make efficient use of available roof area, especially in urban or densely populated areas. Aesthetic Considerations: Advantage: Rooftop installations are often less obtrusive and may be more visually appealing, especially if you are concerned about the aesthetics of your property. Energy Efficiency: Advantage: Rooftop systems can be more energy-efficient due to their proximity to the point of use. There are fewer transmission losses compared to ground-mounted systems. Permitting and Zoning: Consideration: Check local permitting and zoning regulations. Rooftop installations may have fewer regulatory hurdles compared to ground-mounted systems. Shade and Obstructions: Consideration: Ensure that your rooftop receives adequate sunlight throughout the day. Shade from nearby buildings or trees can significantly impact the performance of rooftop solar panels. Structural Integrity: Consideration: Assess the structural integrity of your roof. Ensure that it can support the weight of solar panels and withstand the additional load, especially in areas prone to heavy snow or strong winds. Installation Costs: Consideration: Installation costs for rooftop systems are generally lower because they utilize existing structures. However, factors like roof condition and orientation can affect costs.
Ground-Mounted Solar System:
a. Available Land: Advantage: Ground-mounted systems are suitable for properties with ample available land. This option is more feasible for larger-scale installations.
b. Optimal Sun Exposure: Advantage: Ground-mounted systems can be positioned to optimize sun exposure, especially if the orientation and tilt of your roof are not ideal for solar panels.
c. Maintenance Accessibility: Advantage: Ground-mounted systems are often easier to access for maintenance and cleaning, as they are at ground level.
d. Potential for Tracking Systems: Advantage: Ground-mounted systems may allow for the use of tracking systems that follow the sun's path, optimizing energy production throughout the day.
e. Roof Integrity: Consideration: If your roof is not suitable for solar panels or requires extensive modifications, a ground-mounted system may be a more practical option.
f. Potential for Expansion: Consideration: Ground-mounted systems offer more flexibility for expansion if you plan to increase your solar capacity in the future.
g. Installation Costs: Consideration: Ground-mounted systems can have higher installation costs due to the need for additional infrastructure, such as support structures and foundations.
Hybrid or Dual Systems:
a. Combining Rooftop and Ground-Mounted: Advantage: In some cases, a combination of rooftop and ground-mounted systems might be the optimal solution. This approach allows for maximizing energy production by using available roof space and utilizing additional land.
b. Energy Storage Integration: Consideration: If you are considering energy storage solutions (such as batteries), evaluate whether rooftop or ground-mounted systems are more conducive to integrating storage technology based on available space and access. Ultimately, the best choice depends on your specific circumstances, goals, and constraints. Consulting with a reputable solar installer and conducting a thorough site assessment can help determine the most suitable installation type for your needs.

6.Excess production of solar energy.
The production of solar energy more than our needs might be one of the problems that everyone would like to face. Solar energy systems normally hit the highest electricity production in the afternoon, when many people aren’t home using electricity. In other words, home electricity use is typically more in the mornings and evenings. There is a way to save that excess production and convert it into money. the process is called Net Metering. It will help you in the ups and downs of electricity production. This mechanism called net metering. This billing system was designed and implemented as a benefit to encourage the acceptance of solar systems in both the residential and commercial sectors.

7. some important facts about solar
Here are some important facts about solar energy and solar panels based on the search results:
1. Solar power is the Earth's most abundant energy source, with more solar energy hitting the Earth in a single hour than all humanity needs for an entire year.
2. Solar energy has been used for more than 2,700 years for heating, cooking, and other essential applications that make our lives more efficient.
3. The modern photovoltaic (PV) cell was developed by Bell Labs in 1954, marking a significant advancement in solar technology.
4. Solar power has leaped into prominence as the fastest-growing sector of the energy economy, creating jobs at six times the rate of the general job market.
5. Solar panels can last up to 30 years.
6. Solar energy is virtually inexhaustible and the most abundant source of energy on Earth.
7. Solar energy is one of the most popular renewable energy sources on the planet, yet less than 5% of electricity produced globally comes from solar power.
8. Solar power is the cheapest energy source.
9. Solar energy is environmentally friendly, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and reliance on fossil fuels.
10. Solar energy technology has significantly improved, making solar cells cheaper and easier to produce, leading to their widespread use in rooftops and large solar farms.
These facts highlight the importance and potential of solar energy as a renewable and sustainable energy source.

8. Variety of Warranties in Solar
Solar panel warranties typically include a product warranty and a performance warranty. The product warranty covers the equipment and typically guarantees at least 10-12 years without fail, while the performance warranty guarantees the panel production capability will not drop below a specified level for 25-30 years. Solar installation warranties can range from around five years up to 25 years, and they cover issues related to other components such as racking and wiring. In addition, some solar installation companies offer additional warranties/guarantees in addition to what the manufacturer provides. It's important to understand the difference between the manufacturer's warranties and what your solar installation company guarantees. Other components such as inverters, batteries, and racking have their own product warranties, which are generally shorter than solar panel warranties.

9. The production Process of solar energy
The production process of solar energy involves several key steps, primarily in the manufacturing of solar panels. Here is an overview of the process based on the provided search results:
a. Silicon Purification: The first step in solar panel manufacturing is purifying the silicon from quartz sand. This process requires a significant amount of energy and cost.
b. Ingot Formation: Once the silicon is purified, it is collected into solid rocks and then molten together to form cylindrical ingots using a steel and cylindrical furnace.
c. Wafer Production: The cylindrical ingots are then sliced into thin wafers. These wafers are treated, and metal conductors are added to create a grid-like matrix on the surface, which facilitates the conversion of solar energy into electricity.
d. Solar Cell Assembly: The treated wafers are then assembled into solar cells, which are capable of converting solar power into electricity.
Solar Panel Manufacturing: Solar panels are made by assembling solar cells, glass, EVA (ethylene-vinyl acetate), backsheet, and frame. The solar cells are typically made from silicon or another semiconductor material and are installed in a metal panel frame with a glass casing. The process of solar panel manufacturing is energy-intensive, particularly during the silicon purification stage. However, once the panels are manufactured, they can last up to 30 years and provide a renewable and abundant source of energy.